“If it never rained, we’d have great water quality in Iowa.”
-Jim Richardson
“If it never rained, we’d have great water quality in Iowa,” joked a volunteer at our May 15 water quality snapshot. 15 of us spent the morning testing Ioway Creek and its tributaries in Boone, Hamilton, and Story County and were marveling at the low nitrate levels and crystal clear water at the majority of our sites.
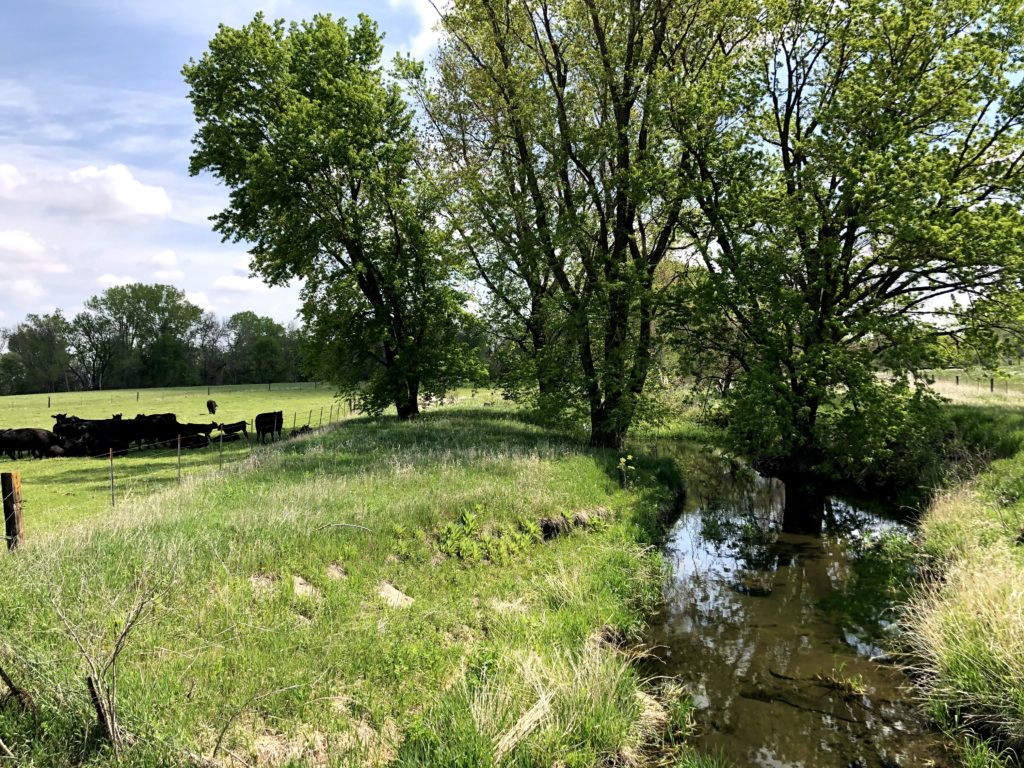

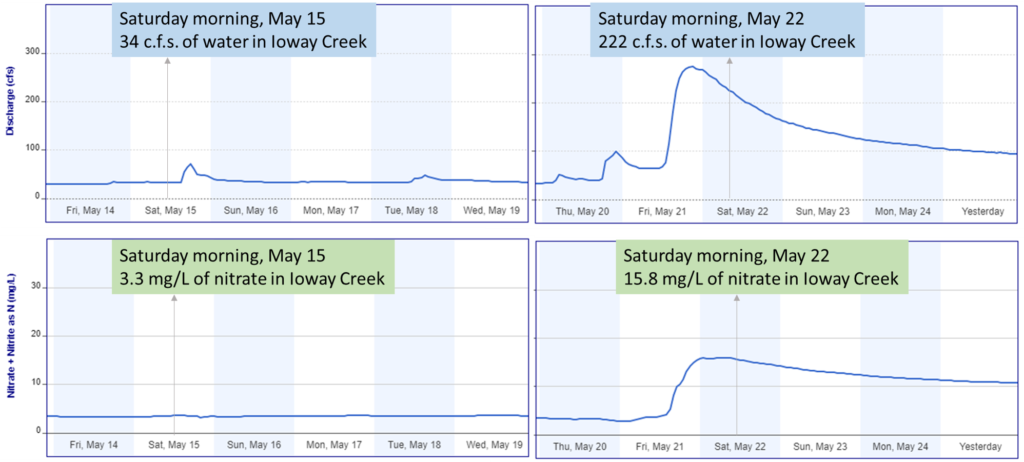
Well, we’ve had some much-needed rain in the week since, and water quality has gone from good to bad. I’ve written before about “weather whiplash” that explains some of the big swings in nitrate over the past decade and here’s an early hint of it. Here’s data from a nitrate sensor in Ioway Creek installed by IIHR-Hydroscience and Engineering. A five-fold increase in nitrate concentrations in just one week! The water has gone back down but the nitrate levels are still above the drinking water standard.
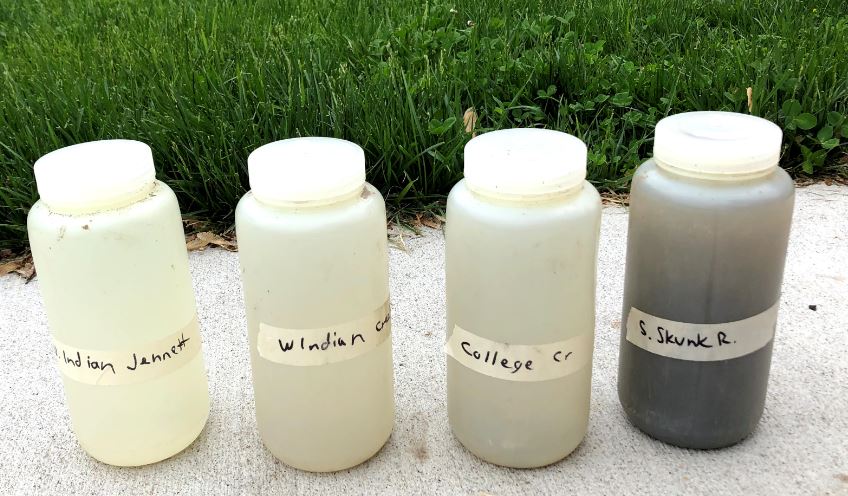
And here’s some water samples I collected on Friday May 21. No, that’s not my coffee thermos, that’s some of the world’s best top soil washing down the Skunk River!

That’s not to blame the weather. It does rain in Iowa and if your farming practices let a plume of topsoil, manure, or fertilizer wash off the field every time that happens, you’re doing it wrong! Some farmers are doing it right (I saw some cover crops this spring near Nevada and lots driving on I-80) but not enough, especially in the Ioway and South Skunk River watersheds.
Water quality monitoring has been top of mind for Prairie Rivers of Iowa lately and I see an challenge and an opportunity. It’s a challenge to interpret data and track our progress when one good rain can cause water quality to go from clear to coffee-colored overnight! There’s an opportunity to be more strategic about how and where we test, so we notice and communicate more eye-opening moments like this one, and hopefully persuade a few more people to protect soil and water.
Update: June has been abnormally dry and Hamilton, Boone and Story County are experience severe drought. Droughts stress is impacting crops and smaller streams are drying up.
